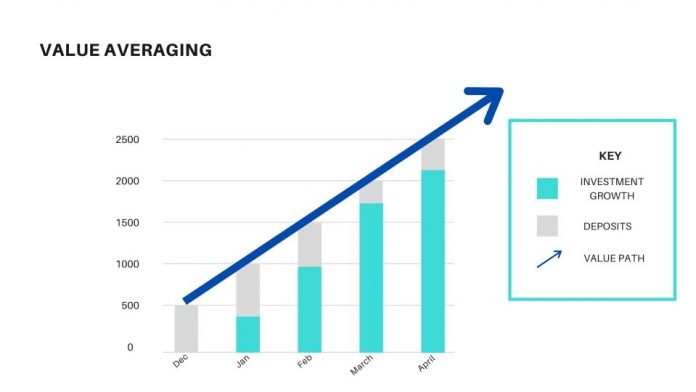
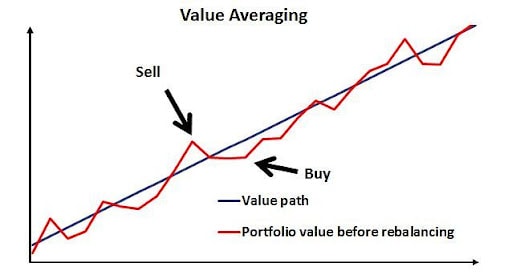
Value Averaging is an investment technique that takes on more shares when stocks are low, and less or none, according to a set term portfolio increase, when stocks are high, leading to lower costs per share on average, and more shares in possession when prices fall. The overall goal is to see a portfolio’s worth increase over time with little spending.
What is Value Averaging in Stock Trading?
Value averaging is setting a term portfolio increase, and buying shares of stock accordingly, if necessary.
For example, suppose that an investor’s portfolio is worth $1,000. He could decide to see it increase by $100 per month, and after one month, if it is not worth $1,100 total, he will buy shares of stock to contribute to the portfolio so that it increases by the full $100. For example, if, after the first month, the portfolio is worth $900, the trader will take on $200 worth of stock, adding them to the portfolio.
If it is worth $1,050 after the first month, he will take on $50 worth of stock. And if the overall worth is at or above $1,100 after a month, no stock is taken on (in fact, depending on strategy, some shares could be sold), as the monthly increase has been reached.

After the second month, according to the value averaging plan in this example, the portfolio will need to be worth at least $1,200, or else the trader will invest however much is needed to make it worth $1,200 (1,200-portfolio value).
What is a Fill Or Kill Order in Stock Trading?
What is a Stock Trading Alternative Order?
Point of Value Averaging in Stock Trading
The point of value averaging in investing is to see a portfolio’s worth increase by set amounts periodically. This can lead a trader to take on shares when securities drop, to add to a portfolio’s overall strength in buying low, or averaging down.
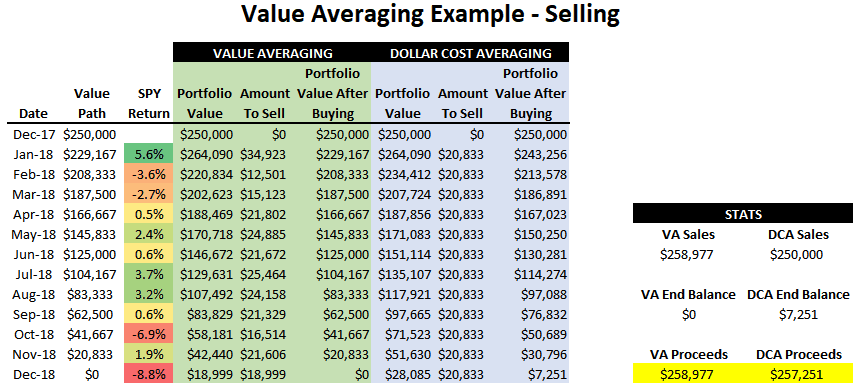
If, for example, more of the same securities that are in the account are taken on when the portfolio falls in value from one month to the next, the average cost per share will be lowered, as when the portfolio has decreased in value, it means that shares are trading for less than before.
Trading with the same stock is not a requirement, however. The only requirement in value averaging in stock trading is that an investment portfolio increases by the set amount each term, either by well-performing stocks, or by investment contributions.
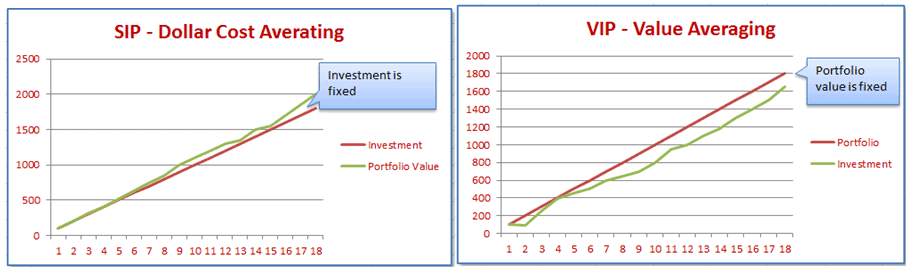
Value averaging simply sees an investment portfolios worth increase over time. This can mean buying additional stock when it does not increase enough, to increase its overall worth, effectively buying stocks when they are down, and buying few or none when the value of the portfolio is up, as stocks are trading well and may be costly.